Hot Products


POCHONIA CHLAMYDOSPORIA
Effective treatment for root knot nematode control in soybean cyst
POCHONIA CHLAMYDOSPORIA,Effective treatment for root knot nematode control in soybean cyst
Pochonia chlamydosporia, also known as Verticillium chlamydosporium. It is a fungus that has gained attention for its potent ability in root knot and soybean cyst nematode control. By colonizing and producing spores, the fungus infect and kill eggs. The best nematicide for plants is a promising bio control agent for its effectiveness against different species. Similar to Metarhizium anisopliae, it persists in soil and organic debris, making it an eco-friendly solution for farmers. Where to buy nematode control products, Novobac is your go-to manufacturer.
hiddenValue
USE FOR
MODE OF ACTION
TECHNICAL
BENEFIT
INSTRUCTION
DOCS
-
USE FOR
Target Insect
• Root-knot (Meloidogyne spp.)
• Cyst (Heterodera and Globodera spp.)
• Lesion (Pratylenchus spp.)
• Reniform (Rotylenchulus spp.)
COMMON CROPS

corn

wheat

rice

broad beans

vegetables

tomatoes

cabbage

peppers
-
MODE OF ACTION
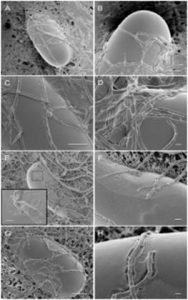 Infection and parasitism of eggs: The best nematicide for plants infects and parasitizes the eggs, preventing their hatching or reducing their viability. The fungus produces specialized structures called chlamydospores that germinate and penetrate the eggshell, invade the developing embryo, and consume its nutrients, leading to its death.
Infection and parasitism of eggs: The best nematicide for plants infects and parasitizes the eggs, preventing their hatching or reducing their viability. The fungus produces specialized structures called chlamydospores that germinate and penetrate the eggshell, invade the developing embryo, and consume its nutrients, leading to its death.- Enzymatic degradation of cuticle: Produces enzymes proteases and chitinases breaking down the cuticle and facilitate fungal invasion. This enables the fungus to colonize and consume the tissues, leading to its death in soybean cyst nematode control.
- Production of secondary metabolites with nematicidal activity: Secretes secondary metabolites such as polyketides, terpenoids, and alkaloids. The metabolites have nematicidal activity and kill nematodes directly. These compounds disrupt its physiology and metabolism, leading to its death.
-
TECHNICAL
AVAILABLE SPECIFICATION
Bacteria count : 1 x 10^9 cfu/g
MANUFACTURER
Novobac, a Leading Supplier Providing Sustainable Agriculture with Organic Micro-Based solutions
FORMULATION TYPE
Wettable powder
PACKAGING
1 kg or 25 kg per bag
SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
24 months when stored properly in a cool and dry place.
keep out of direct sunshine and moisture.
Once opened, use it within 30 days.
Stay away from children.
-
BENEFIT
Benefit
- Offers a sustainable method for soybean cyst control without resorting to chemical pesticides.
- Be used in organic farming and is considered safe for humans and the environment.
- Reduces crop losses and increase yield by preventing damage to roots.
- A wide range of hosts and can infect multiple species, making it a bio control agent.
- Survives well and can persist beyond the growing season, providing long-term nematode control.
- Improves soil quality by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients that are beneficial to plants.
- Does not harm non-target organisms such as beneficial insects, earthworms, or microorganisms.
- Reduces the risk of developing resistance among the populations, unlike chemical pesticides that can create resistant strains over time.
See different for yourself
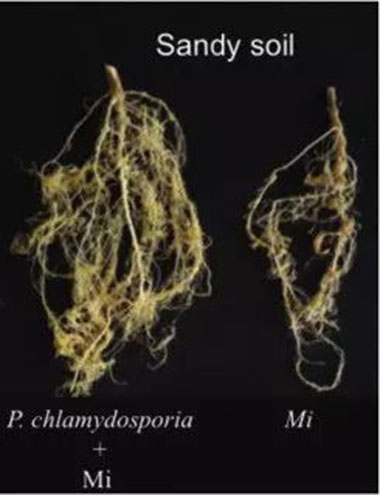
Effect in Sandy Soil
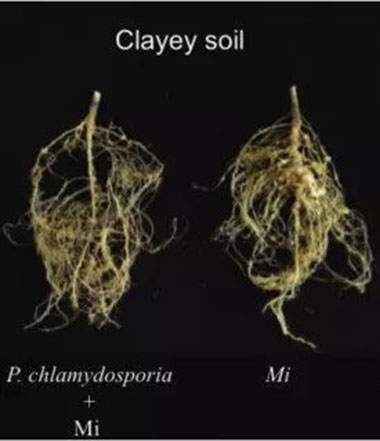
Effect in Clayey Soil
-
INSTRUCTION
Application Rate
- For soil application, the recommended dosage is 500-1000 grams per hectare, mixed with other organic matter and applied before planting.
- For containerized crops, the recommended dosage is 10-20 grams per cubic meter of growing medium, mixed thoroughly before planting.
- For maximum benefits of nematicide for plants, the optimal temperature range is between 20-30°C. It also require soils with pH range of 5.5 to 7.5 and moisture content with range of 50-75% of field capacity.
What management practices can improve the effectiveness of Pochonia chlamydosporia?
- Soil solarization: Exposing soil to high temperatures can help reduce nematode and increase the effectiveness of nematicide for plants.
- Use of organic amendments: Organic materials such as compost bio fertilizers improve the nutrient content and structure of soil. This promotes the growth of best nematicide and effectively controls soybean cyst.
- Use of resistant crop varieties: Planting crop varieties that are resistant or tolerant to nematodes reduce the damage caused by these pests.
- Biological control agents: Using other good micro organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and predatory nematodes complement its action and provide long-term control.
- Cultural practices: Practices like deep plowing, weed management, and avoiding overwatering can help promote healthier root systems.
- Crop rotation: Growing different crops in a field over time can help disrupt the life cycle, reducing their populations.
- Deep tillage: Tilling the soil to a depth of at least 15 cm (6 inches) can help expose nematodes to stressors. This nematode control products can also improve soil structure and promote root growth.
- Soil pH management: Maintaining pH within the optimal range for the nematode control products (around 6.0-7.5), leading to better control of nematodes.
- Avoidance of chemical pesticides: Chemical pesticides can harm beneficial microorganisms in soybean cyst nematode control, reducing effectiveness of nematicide for plants.
-
DOCS



CONTACT US

Office 38/1502, No 660,Hanguang Rt., Changsha City, Hunan, China