Hot Products


STREPTOMYCES MICROFLAVUS
Natural antifungal for plants with bioactive compounds improve soil structure
STREPTOMYCES MICROFLAVUS,Natural antifungal for plants with bioactive compounds improve soil structure
Streptomyces microflavus is a soil bacterium with numerous benefits, making it valuable in sustainable agriculture. It fixes atmospheric nitrogen, produces antibiotics, breaks down organic matter, and improves soil structure. This natural antifungal for plants can also suppress soil-borne pathogens, leading to better soil quality and increased crop yields. It helps maintain soil fertility by converting inert atmospheric nitrogen into biologically available forms for plants. Trusted manufacturers like Novobac offer Streptomyces microflavus products.
hiddenValue
USE FOR
MODE OF ACTION
TECHNICAL
BENEFIT
INSTRUCTION
DOCS
-
USE FOR
Target Disease
• Fusarium wilt • Rhizoctonia root rot • Phytophthora blight • Verticillium wilt Antagonistic Activity
One of the applications is in the production of bioactive compounds such as antibiotics, enzymes, and metabolites that have the ability to inhibit the growth of harmful fungi and bacteria. These compounds are pet safe which can target specific pathogens and disrupt their cellular processes, preventing them from infecting plants or causing disease symptoms.
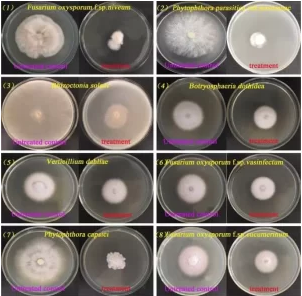 (a) Fusarium oxysporum f.sp niveum
(a) Fusarium oxysporum f.sp niveum(b) Phytophthora parasitica
(b) Rhizoctonia Solani
(c) Botryosphaeria dothidea
(d) Verticillium dahlia
(e) Fusasrium oxysporum f.sp vasinfectum
(f) Phytophthora capsici
(g) Fusarium oxyporum f.sp cucumerimum
-
MODE OF ACTION
- The natural antifungal for plants produces bioactive compounds that exhibit antagonistic activity against various plant pathogens. These compounds can inhibit the growth of harmful fungi and bacteria responsible for plant diseases by targeting specific cellular processes, such as cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or DNA replication.
- It produces a wide range of bioactive compounds, including antibiotics, enzymes, and metabolites that can act as antifungal, antibacterial, or antiviral agents. These compounds can either kill the pathogen directly or disrupt its cellular functions, preventing it from infecting plants or causing disease symptoms.
- In addition to its direct antimicrobial activity, the pet safe fungicide can also induce systemic resistance in plants. This process involves triggering the plant’s defense mechanisms and enabling it to produce phytohormones and other biochemicals that enhance its immunity system. This response helps the plant to fight off infections and resist pathogen attacks.
-
TECHNICAL
AVAILABLE SPECIFICATION
Bacteria count 3* 10^9 CFU/g
FORMULATION TYPE
Wettable Powder
PACKAGING
1 kg or 25 kg per bag
SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
It has a 24-month shelf life and should be dried and cold, away from moisture and sunlight, to maintain its effectiveness. Use the product within 30 days of opening for the greatest results. Please take the necessary steps to keep the product out of children’s reach.
-
BENEFIT
Benefit
- Broad-spectrum pesticide available for organic pest control
- Environmentally friendly and organic antifungal for plants
- Safe for use in various agricultural settings
- Does not cause drug resistance in pests
- Enhances plant health and production by aiding nutrient uptake
- Offers persistent defence mechanism against future infestations
- Valuable tool for sustainable agriculture practices to reduce pesticide use while improving crop yields.
-
INSTRUCTION
Application Rate
- Foliage spray: 2-3 grams per liter of water
- Soil application: apply 2-3kg per hectare to soil around base of each plant
- Pre-transplanting: 2 kg of the pet safe fungicide and 20 kg of farm yard manure per acre of main field
How does streptomyces fungicide help the soil?
- Nitrogen fixation: It is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen, which makes it available for plant uptake.
- Disease suppression: Plant diseases are less likely because of the antibiotics that are produced by this bacteria, which can reduce soil-borne infections.
- Organic matter decomposition: It break down organic matter, releasing nutrients into the soil that are essential for plant growth.
- Soil aggregation: This bacteria helps to bind soil particles together, improving soil structure and water-holding capacity.
How does it suppress tomato bacterial wilt disease?
The natural antifungal for plants produces antibiotics that inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, induces systemic resistance in tomato, competes with pathogenic bacteria for nutrients, and produces enzymes that degrade cell walls of pathogenic bacteria.
How can it be used to make bioorganic fertilizer?
The bacteria can be used to make bioorganic fertilizer through a process called solid-state fermentation. Here are the general steps involved:
- Select a suitable substrate material: Agricultural waste products like rice straw, wheat bran, or corn cob can be used as substrates for the fermentation process.
- Inoculate the substrate with S. microflavus: The bacterial culture of S. microflavus is mixed with the substrate material and distributed evenly.
- Incubate the mixture: The inoculated substrate is then incubated for a specific duration under controlled conditions, including temperature, humidity, and aeration.
- Harvest the bioorganic fertilizer: After incubation, the fermented substrate material is harvested and dried to produce the bioorganic fertilizer.
-
DOCS


Product Spotlight
CONTACT US

Office 38/1502, No 660,Hanguang Rt., Changsha City, Hunan, China