Hot Products


TRICHODERMA LONGIBRACHIATUM
Fungicide plant spray control anthracnose and other diseases
TRICHODERMA LONGIBRACHIATUM,Fungicide plant spray control anthracnose and other diseases
Trichoderma longibrachiatum is a beneficial fungus that is commonly used to improve soil health and protect crops against soil-borne diseases. The fungicide plant spray also helps to break down organic matter in the soil, making nutrients more available for plant uptake. The anthracnose fungicide drench strain is eco-friendly and safe in tomato blight treatment and root rot treatment. If you’re looking for a natural solution to increase crop yield while reducing chemical inputs, try Novobac’s Trichoderma longibrachiatum powder.
hiddenValue
USE FOR
MODE OF ACTION
TECHNICAL
BENEFIT
INSTRUCTION
DOCS
-
USE FOR
Antagonistic Activity
It produces enzymes that degrade the cell walls of fungi and colonizes the root zone and secretes antifungal compounds.
(a) Alternaria alternata
(b) Rhizoctonia solani
(c) Aspergillus niger
(d) Geotrichum candidum
(e) Fusarium oxysporum
(f) Macrophomina phaseolina
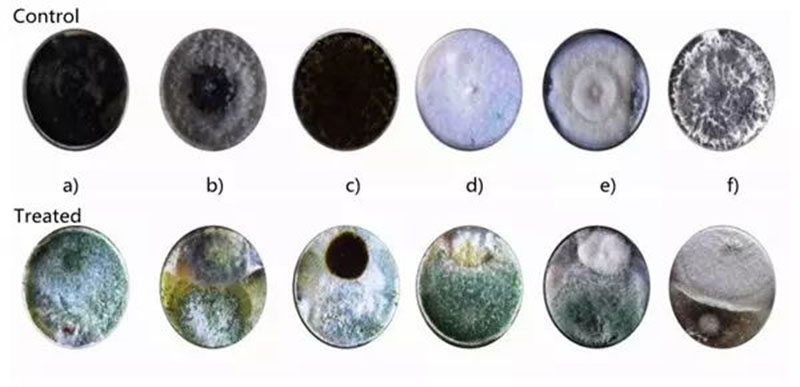
-
MODE OF ACTION
- Induction of plant defense mechanisms: The anthracnose fungicide induces various defense-related genes in plants toactivatedefense mechanisms against pathogenic fungi.
- Competition for nutrients and space: colonizes the root zone, competing with pathogenic fungi for nutrients and space. This reduces the population of pathogenic fungi and promotes plant growth.
- Production of plant growth-promoting substances: produces auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins, which promote plant growth and development.
- Mycoparasitism: can directly attack and parasitize pathogenic fungi, leading to their death. This helps to control plant diseases in tomato blight treatment and root rot treatment.
-
TECHNICAL
AVAILABLE SPECIFICATION
Bacteria count : 5 x 10^9 cfu/g, 1x 10^10 cfu/g
FORMULATION TYPE
Wettable Powder, 100% soluble
PACKAGING
1 kg or 25 kg per bag
SHELF LIFE AND STORAGE
When kept in a clean, dry, and cold atmosphere, 18 months.
Avoid dampness and strong sun.
To eliminate activation after open, utilise it within 30 days.
Avoid kids at all times.
-
BENEFIT
- Biological control: An effective biological control agent against Fusarium, Rhizoctonia, and Pythium. The drench strain colonizes plant roots and generates antifungal compounds to protect them from fungal diseases.
- Plant growth promotion: Increases nutrient availability, enhances root development, and induces systemic resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses.
- Soil health improvement: Improves soil health by decomposing organic matter, releasing nutrients, and suppressing harmful microorganisms in root rot treatment.
- Bioremediation: Degrades pesticides, herbicides, and petroleum hydrocarbons, which makes the fungicide plant spray beneficial for contaminated soil bioremediation.
- Biofertilizer production: Fix atmospheric nitrogen and solubilize phosphorus, making these nutrients available to plants.
-
INSTRUCTION
Application Rate
- Seed Treatment: Mix 1-2 grams with water to make a paste and coat the seeds with the paste before sowing.
- Soil Application: Apply 1-2 kg per hectare mixed with compost or organic manure during crop growth.
- Foliar Spray: Mix 2-5 grams with one liter of water and spray it on the plants using a foliar sprayer.
- Irrigation: Add 1-2 kg to irrigation water and apply it to the crops.
How can I maximize the effectiveness of the product?
- Use high-quality products: Ensure that the product contains viable and active spores in plant management including tomato blight treatment.
- Apply at the right time: Apply the anthracnose fungicide early in the growing season. This allows the fungus to establish a strong relationship with the plant and provide maximum protection against soil-borne diseases.
- Apply to healthy soils: Works best in soils with a diverse microbial population drench strain. If your soil is lacking in beneficial microbes, consider applying soil amendments or organic matter to improve soil health.
- Avoid using fungicides: Fungicides can kill beneficial fungi, reducing its effectiveness. If fungicides are necessary, apply them at a different time or use them sparingly.
- Follow practices: Crop rotation, proper irrigation, and weed management can help reduce plant stress and disease pressure, improving the effectiveness.
- Monitor crop growth and disease pressure: Adjust your management practices accordingly helps you identify when additional applications may be necessary.
-
DOCS


CONTACT US

Office 38/1502, No 660,Hanguang Rt., Changsha City, Hunan, China