Organic Cucumber Pests and Diseases Control Microbial Solutions
- Biological Control
-
- Commodity name: Organic Cucumber Pests and Diseases Control Microbial Solutions
The major raw materials used in salads and sandwiches are cabbages and meats; vegetables which boast of being a gardener’s delight as well as being a commercial farmer’s bank. However, they cannot withstand different pests and diseases that may plague the cucumbers and reduce the yield. The following are the challenges likely to be encountered in the process, all of which require good management in order to have a good harvest of cucumbers.
These are the challenges that a farmer has to factor in if he has to be in a position to produce good cucumbers. You can be certain of a good yield in cucumbers if you effectively apply proper management lessons on them. That way, onerous features affecting the efficiency of cucumber harvesting can be better managed. This is a comprehensive manual of cucumber common pests and diseases and their organic control and bio remedies. Continue reading to know about cucumber pests and diseases treatment.
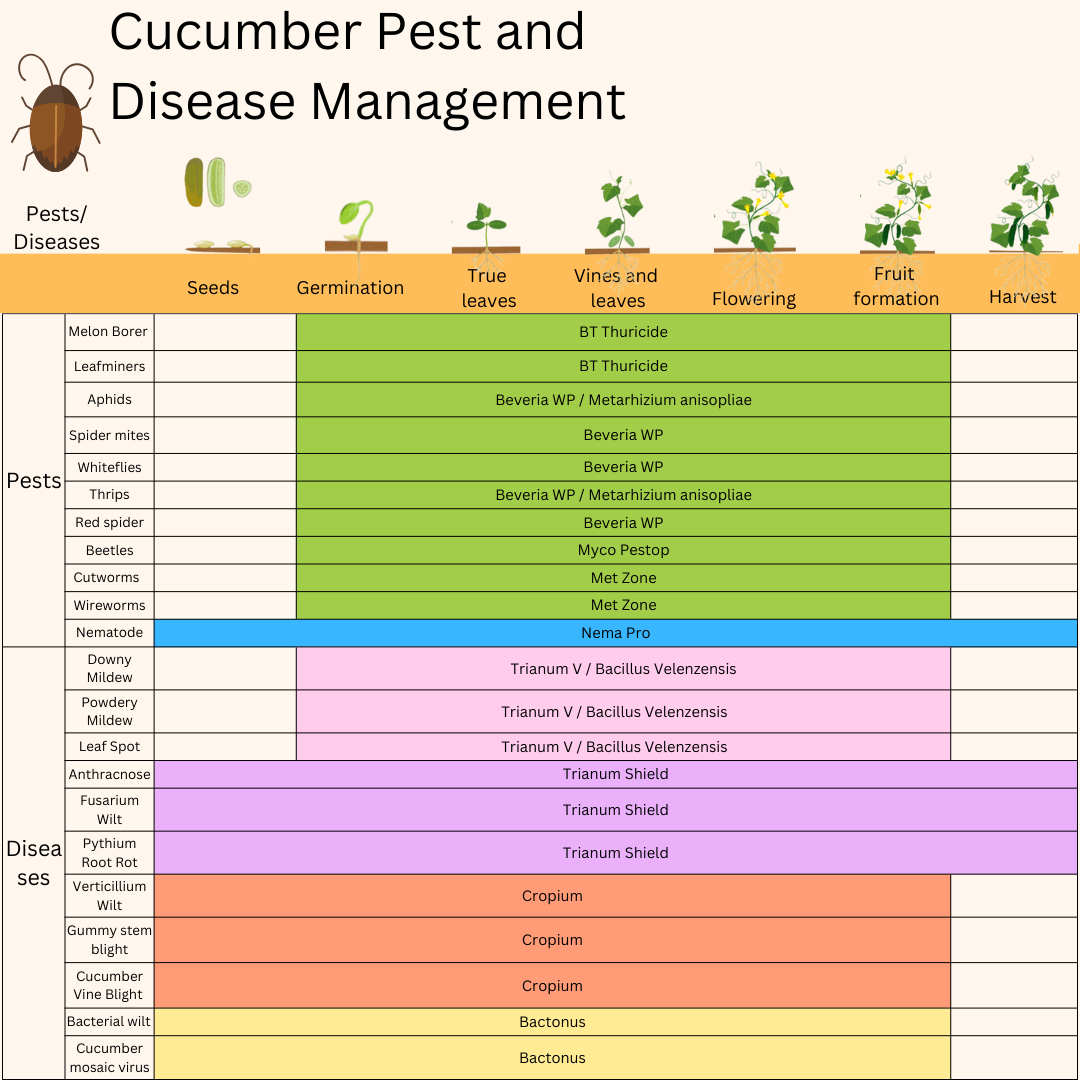
Organic Pest Control For Cucumber
Target Pests: Melon Borer and Leafminers Control
Recommend Product: BT Thuricide
Active Ingredient: Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies kurstaki
 Melon Borer Cucumber Pests
Melon Borer Cucumber Pests Leafminers Cucumber Pests
Leafminers Cucumber PestsBt spraying should be coupled with suitable cultural practices that relate to each development phase of cucumbers. With this product, your plants will benefit from proper cucumber leaf miner treatment and cucumber melon borer control, hence better growth and yield.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
Crop rotation and use of resistant varieties such as cucumber will go a long way in handling melon borer and leaf miner pests.
- Cucumber plants should also be checked for pest signs often.
- Clear the field and surrounding areas of weeds and plant debris so as to deny melon borers and leafminers habitats.
- Organically control through parasitic wasps, lacewings etc for biological control.
- Some plant parts infested with pests should be pruned off and discarded to prevent junior infestation.
- Use attractants such as Diatomaceous Earth Food Grade, Smuggler Baits, or other dual bait type products to go after the active pest larvae with Heliconca Insecticides like BT Thuricide, Beauveria bassiana or any Pyrethrin-Based Products.
Target Pests: Aphids, Spider Mites, Whiteflies, Thrips, and Red Spider Control
Recommend Product: Beveria WP
Active Ingredient: Beauveria Bassiana
 Aphids Cucumber Pests
Aphids Cucumber Pests Spider Mites Cucumber Pests
Spider Mites Cucumber Pests Whiteflies Cucumber Pests
Whiteflies Cucumber Pests Thrips Cucumber Pests
Thrips Cucumber Pests Red spider Cucumber Pests
Red spider Cucumber PestsBeveria WP is a biologically derived insecticide containing Beauveria bassiana which is an entomopathogenic fungus which infects a multitude of soft bodied insects and mites. Here follows a pest management check-list based on growth stages of cucumbers using Beveria WP and practices for healthy plants.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Crop Rotation: Cucumbers should be planted in a different field with crops that the pest does not prefer or impact on its reproduction.
- Companion Planting: For your information; instead of relying in chemical pest control; grow marigolds or dill near your plants so that you can repel pests through the green vegetables.
- Early Detection: Pests in cucumbers should be checked often especially if it is warm and humid in the growing environment.
- Healthy Soil: Compost is also required, and the content of nutrients in the ground must not be very high to improve the plants’ capability to fight pests.
- You should treat your cucumber plants with Beveria WP and Beauveria Bassiana for biological control of aphids, spider mites, whiteflies, thrips, and red spiders.
Target Pests: Cucumber Beetles Control
Recommend Product: Myco Pestop
Active Ingredient: Metarhizium anisopliae
 Cucumber Beetles Cucumber Pests
Cucumber Beetles Cucumber PestsMyco Pestop formulated for cucumber beetle eradication and launched with bio-pesticide Metarhizium anisopliae works effectively in infecting beetles and killing it during its life cycle. Herein is a pest management calendar for each stage of cucumber growth with Myco Pestop and proper cultural practices.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Crop Rotation: Do not reorder cucumbers successively with companion crops such as squash and corn because they are the beetle hosts.
- Companion Planting: Plant flowers that repel beetles; marigolds or tansy are good examples of plants that act as repellents to beetles.
- Sanitation: Do not grow weeds, plant debris or fallen fruits and nuts in the fields as these act as a breeding ground of beetles.
- Natural Predators: Support development of carnivorous beneficial insects including parasitic wasps and lady beetles.
- Using natural insecticides: You should use an insecticide like Myco Pestop or Metarhizium anisopliae to fight beetles affecting your cucumber plants.
Target Pests: Cutworms and Wireworms Control
Recommend Product: Met Zone
Active Ingredient: Metarhizium anisopliae
 Cutworms Cucumber Pests
Cutworms Cucumber Pests Wireworms Cucumber Pests
Wireworms Cucumber PestsMet Zone a biological insecticide that uses Metarhizium anisopliae gives secure soil inhabiting pests hence is efficient in cucumber cutworms control; cucumber wireworm control. Cutworms and wireworms, for instance, pose a serious threat to young plants of cucumbers and at times cause nearly complete devastation. The following are pest management recommendations at different stages of cucumber production by using Met Zone together with proper cultural operations for health crops.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Soil Preparation: To eradicate cutworms and wireworms, cultivate before planting then destroy the pests.
- Crop Rotation: Cucumbers should not be planted in fields that had been used by cutworms and wireworms host crops such as potatoes, carrots etc.
- Companion Planting: Select plants like marigold because they act as a natural wireworm resistant.
- Trapping: Some bait methods include; placing pieces of vegetables such as potatoes arranged on the soil surface or buried slightly to check for the presence of wireworms and physically pulling them out.
- Monitoring: Check the bottom of the plant and/or soil for pest signs as these are most likely to be seen in such conditions.
- Biological Control: Since pest pressure could be influenced by the plant density, Met Zone should be applied at regular intervals on the soil especially on the critical growth stage of the plants.
Nematode Control for Cucumbers
Target: Nematode Biocontrol
Recommend Product: Nema Pro
Active Ingredient: Purpureocillium Lilacinum
 Nematode Cucumber Pests
Nematode Cucumber PestsNema Pro nematodes control pesticide containing the natural fungus; Purpureocillium lilacinum [previously called acrodynium Paecilomyces lilacinus] provides an efficient organic control of plant parasitic nematodes in cucumbers. This bio-product an outcompets nematodes for food resources by attaching itself to the mouths of the eggs, larvae and adult forms which are present in the soil and thus reduces the damage caused to cucumber roots by these tiny worms. Following is the guide to stage specific nematode control using Nema Pro incorporated with GAP for better health of crop.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Crop Rotation: Crop rotation should also be carried out with non-host or resistant crops such as corn, millet, or marigold. Such crops interfere with the nematode’s life cycle and rein in the infestations.
- Cover Crops: Sow cover crops such as mustard or sunn hemp, which are bio fumigant crops used in controlling nematode soil borne pests. Fall sow green manure to help regulate nematodes for controlling chilli nematode populations.
- Soil Health Management: Amend the soil with organic supplements by either adding compost or vermiculture that enhances soil microbial community comprising Purpureocillium lilacinum.
- Mulching: Organic mulching should be employed to control soil heat and water After a while, nematode infestation is controlled as the cover shields the roots from pressure.
- Biological Control: As a soil treatment, use Nema Pro at planting time or whenever the development of good fungal sources are desired to colonize the soil and impede nematodes. They should be re-hashed where isolations are desirable to enhance the firm’s control after significant growth phases.
Organic Disease Control For Cucumber
Target Diseases: Downy Mildew, Powdery Mildew, Leaf Spot Treatment
Recommend Product: Trianum V
Active Ingredient: Trichoderma harzianum
 Powdery Mildew
Powdery Mildew Downy Mildew
Downy Mildew Leaf Spot
Leaf SpotTrianum V is a biocontrol agent, helpful for cucumber leaf diseases treatment and is derived from the ASO beneficial fungus Trichoderma harzianum. It helps with treatment of downy mildew, powdery mildew and leaf spot in cucumbers. This wonderful product does this by fixing onto the surfaces of plants, crowds out pathogens, and prop up the inherent defenses that plants have against diseases. It is important to note that different stages of cucumber development have different management mechanisms, here is a stage specific management guide on cucumber leaf diseases and how Trianum V when combined with best cultural practices promotes healthier and more productive cucumber crops.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Field Sanitation: Timely clearance of crops residues and fallen leaves will go a along way in eradicating disease causing organisms.
- Crop Rotation: Space and rotate cucumbers with other crops that do not host the disease such as legumes grains etc.
- Irrigation: Do not wet the foliage through flooding use drip or furrow irrigation instead. Water in the morning to allow the leaves to dry during the day and evening.
- Resistant Varieties: Plant disease resistant cucumber varieties whenever they are available.
- Early Detection: Mildews, leaf spots may occur on the plants during the growing period, and therefore the best solution is to perform frequent inspections in an effort to control its spread.
- Biological Control: Trianum V has got to be used at the beginning of the growing cycle in order to prevent plants from being vulnerable to harm by negative fungi.
Organic Cucumber Soil Borne Disease Control
Target: For Controlling Anthracnose, Fusarium Wilt, and Pythium Root Rot
Recommend Product: Trianum Shield
Active Ingredient: Trichoderma Harzianum
 Anthracnose
Anthracnose Fusarium Wilt
Fusarium Wilt Pythium Root Rot
Pythium Root RotTrianum Shield, the effective fungipermite containing the friendly fungus Trichoderma harzianum, is used to control dangerous soil-borne diseases that affect cucumbers, including the cucumber anthracnose treatment, cucumber fusarium wilt treatment and use as pythium root rot in cucumbers. It functions through root zone control, mycopathogen control, and improved plant health . The following is a stage by stage guide on disease control, using Trianum Shield in combination with other practices to ensure that soil and plant health in your cucumber fields are in their best condition.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Crop Rotation: Do not cultivate cucumbers in one field consecutive season to disrupt the life cycle of pathogens prevalent in that soil.
- Healthy Soil Management: Use organic composts, well-aerated soils, and the like. Soil acidity should be within 6.0 – 7.0 to support friendly microbial growth.
- Sanitation: Remove plant debris and fallen fruits frequently because they are reservoirs of realizing pathogens.
- Water Management: Water the plants moderately, avoid over watering as this favours fungal attack especially Pythium and Fusarium.
- Resistant Varieties: If there are released cucumber cultivars with resistance to specific soil-borne diseases, then they should use them in the program.
- Biological Control: The instant mode of Trianum Shield should be used when planting or early in the plant development stage to capture the root region and shield them from undesirable fungi.
Target: For Controlling Verticillium Wilt, Gummy Stem blight, and Cucumber Vine Blight
Recommend Product: Cropium
Active Ingredient: Penicillium Bilaiae
 Verticillium Wilt
Verticillium Wilt Gummy Stem Blight
Gummy Stem Blight Cucumber Vine Blight
Cucumber Vine BlightCropium, which is derived by adding Penicillium bilaiae fungus, is a Biofungicide for soil borne and vine diseases such as Vorticillium Wilt, Gumy Stem Blight and Cucumber Vine Blight. The active ingredient acts by increasing nutrient absorption particularly phosphorus and encouraging root growth and inhibitation of disease-causing pathogens. The stage-wise management guide of Cropium along with the cultural practices to control these destructive diseases in cucurbits is as follows:
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Crop Rotation: Cucumbers should not be grown in the same place two successive seasons. Crop rotation with crops that are not hosts of the disease such as legumes, cereals so that the pathogens do not build up on the crop.
- Field Sanitation: This call for removing plant parts and other plant debris anticipating reinfection from the diseases to be removed.
- Trellising: Tie cucumber vines so that they do not come into contact with the soil. This is helpful in controlling development of diseases such as Cucumber Vine Blight which is related to the soi
- Irrigation Management: Do not water the plants with overhead irrigation as this makes the leaves and stem wet and in the process making them develop fungal infections.
- Soil Health: Use organic manure and composting methods so as to retain the microbial activities in the field. Appropriate fertilization lowers stress therefore minimizing plant diseases.
- Early Monitoring: Source scouts crops daily for wilting, stem lesions or blight, which may indicate an infestation. Such hosts can cause spread of infection to healthy plants within the growing area from affected parts by early identification and removal.
- Biological Control: Use Cropium at planting or early growth stages to increase root size and efficiency, absorption of nutrients and to inhibit the disease causing organisms.
Target: For Controlling Bacterial Wilt and Cucumber Mosaic Virus
Recommend Product: Bactonus
Active Ingredient: Bacillus safensis, Bacillus velezensis, and Pseudomonas chlororaphis
 Bacterial Wilt
Bacterial Wilt Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV)
Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV)This triple acting bio-product works by containing two strains of Bacillus safensis SER-116, Bacillus velezensis 14 and Pseudomonas chlororaphis 007 and can control Bacterial Wilt as well as Cucumber Mosaic Virus (CMV). These useful bacteria and microbes reduce the disease causing agents, improve the immunity level of body, and improve the health conditions of plants. Herein below is a guide for each stage about how this bio-product should be taken alongside other vibrant farming practices to address these difficult diseases.
Integrated pest management(IPM):
- Vector Control (for CMV):
Mites and aphids transmit Cucumber Mosaic Virus and the latter transmits it directly. Sometimes, aphids are found within greenhouses and using yellow sticky traps can help identify their presence and level of infestation; using organic aphid control (insect predators such as lady beetles).
- Control more weeds also like milkweed and chickweed because they host viruses and, in turn, attract the aphids.
- Crop Rotation: Cycle cucumbers with non-susceptible crops such as grains and legumes, solanaceous or other crops likely to be affected by Bacterial Wilt pathogens.
- Field Sanitation: Saprophytic removal and disposal of infected plants should be done in order to reduce the prevalence of both CMV and Bacterial Wilt pathogens.
- Irrigation Management: Bacterial wilt is also encouraged by waterlogging and excessive soil moisture, therefore the two should be avoided. Drip irrigation is preferable since it gives better control.
- Resistant Varieties: Develop and plant disease -resistant/tolerant cucumber varieties, particularly those resistant to Bacterial Wilt and CMV where available.
- Biological Control: Use Bactonus when transplanting or during the early weeks of growth of plants so as to establish root habitation and inhibit pathogenic bacteria.
Conclusion
Responding to the pest and diseases issue in cucumber production is continually evolving. This must be a Latino of good cultural practice, supervision and early intercessional measure. It is possible to recognize the particular dangers to the cucumbers and, with the usage of I ASM techniques, get rid of diseases and pests completely. Always it is better to prevent rather than eradicating them so if you start with the resistant varieties then try to make conditions unfavorable for pests and diseases. With these practices in osób, cucumbers can be grown well without much effects from the above mentioned challenges.
Organic cucumber pests and diseases management
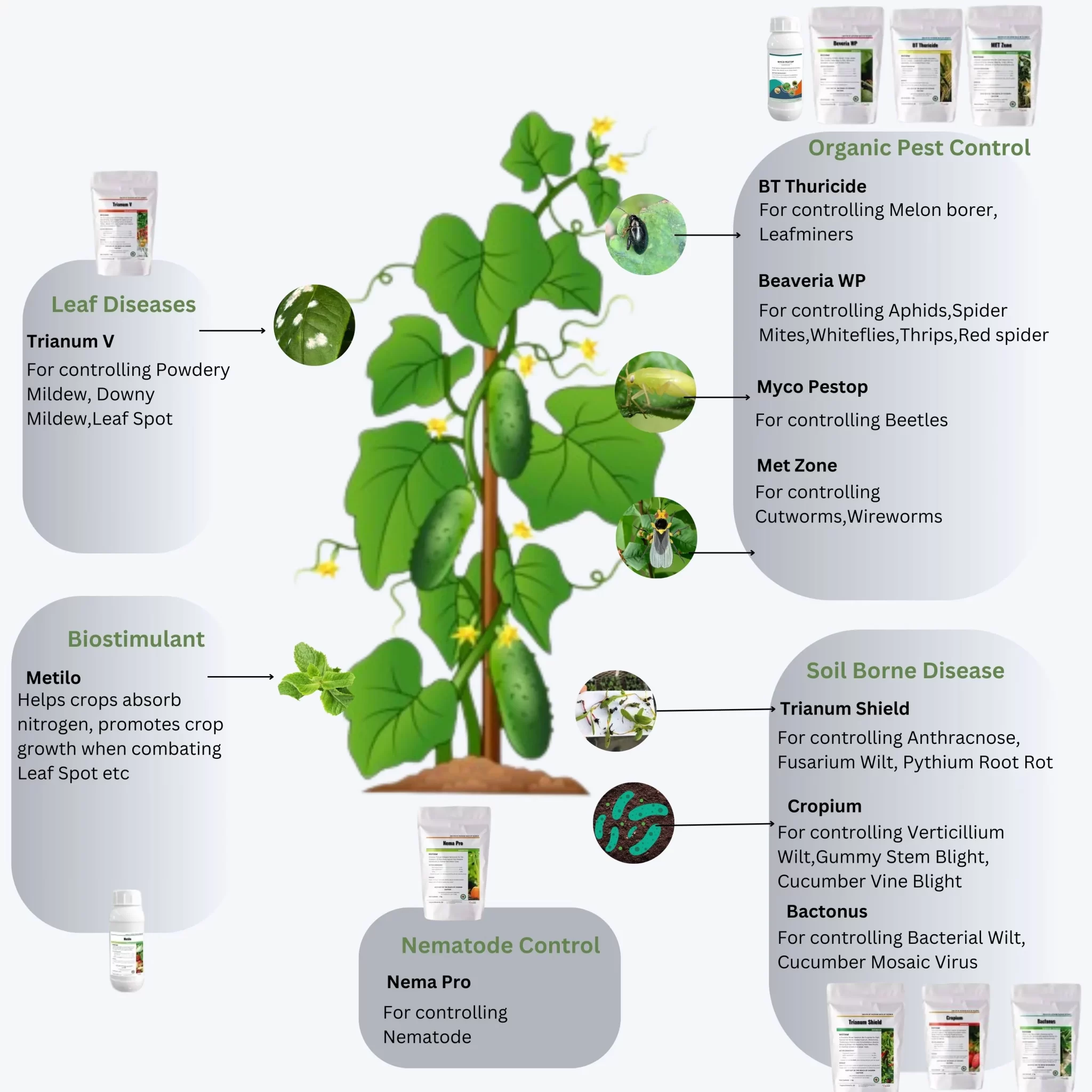
Related Products
CONTACT US

Office 38/1502, No 660,Hanguang Rt., Changsha City, Hunan, China